A szilícium-dioxid ellenőrző téglák bemutatása
Silica bricks are mainly acidic refractory materials composed of tridymite, cristobalite, and a small amount of residual quartz and glass phases.

Functions of checkered bricks
Ellenőrző tégla are widely recognized and accepted by the world’s iron-making community as a heat-carrying and heat-storing body with many superior thermal properties such as strong heat exchange capacity, large heat storage area, smooth ventilation, and low resistance. Checker bricks are a heat transfer medium, mainly used in the middle and upper part of the regenerator of hot blast furnaces to store heat. It plays an extremely important role in the process of heating cold air into hot air.
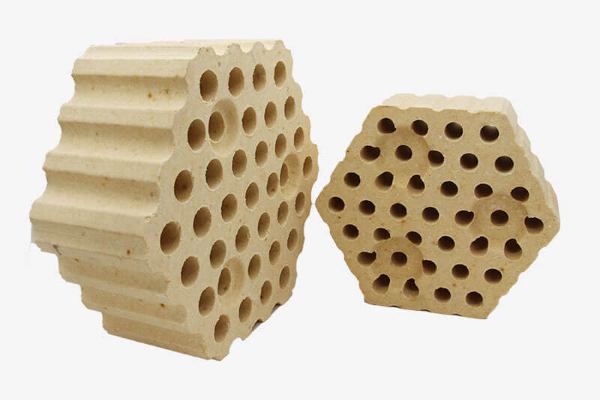
Characteristics of checkered bricks
- It has a plurality of transparent holes parallel to the side surfaces, as well as positioning protrusions and positioning grooves located on the two parallel surfaces.
- Good volume stability, excellent creep performance under high-temperature load, high density, and low porosity. Modern blast furnace hot blast stoves usually adopt a checkered brick regenerator structure.
Application of silica check bricks
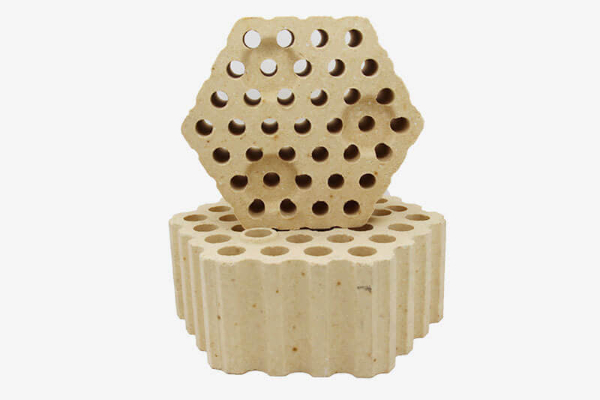

At present, checker bricks are mainly used in blast furnaces hot blast furnaces, and flame furnaces. Checker bricks are mainly used in the regenerator of hot blast stoves. Checker bricks with a certain structure and grid holes are arranged in an orderly manner. The upper and lower holes of the checker bricks can allow gas to pass through. According to different temperature zones or technical requirements, silica check bricks, agyagtéglák, stb. are generally used. In some hot blast stoves, magas timföldtégla, mullite bricks, trichnite bricks, stb. are also selected. The function of the hot blast stove is to turn the blower The cold air sent to the blast furnace is heated into hot air, and then the hot air is sent to the blast furnace through the hot air duct for combustion reaction. The blast furnace hot blast stove has a burning period and a wind-off period, and the two working periods rotate periodically. During the burning period, the burned high-temperature flue gas passes through the holes of the checker bricks of the hot blast furnace and transfers heat to the checker bricks. During the air supply period, the cold air from the blower enters the hot blast furnace and is heated by the checker bricks into hot air and sent to the blast furnace through a hot air duct.
 Rongsheng tűzálló anyagok gyára
Rongsheng tűzálló anyagok gyára
WeChat
Olvassa be a QR-kódot a wechat segítségével